
David Sear, University of Southampton
Britain’s rivers are under the spotlight because of an untreated sewage crisis and the pendulum of floods and droughts that are the hallmark of a warming world. But hidden within these policy debates is a pervasive and under-reported issue: quite simply, people have forgotten what a natural river even looks like.
This is important because it underpins attitudes towards the kind of rivers people expect to live with and constrains the changes to rivers people will be willing to accept. Scientific evidence says radically different-looking rivers are needed to accommodate larger, more frequent floods and droughts, deliver increases in biodiversity, and store more carbon.
Why have we forgotten what our natural rivers look like? In the UK and most other developed economies, the network of streams and rivers has been managed, and physically altered, in some cases, for more than 1,000 years to support more farms and, later, more industry.
It is no wonder most people do not realize that the rivers they grew up with, fish in, swim in, or walk along are nothing like the natural ecosystems they once were. History and culture have evolved around modified river systems.
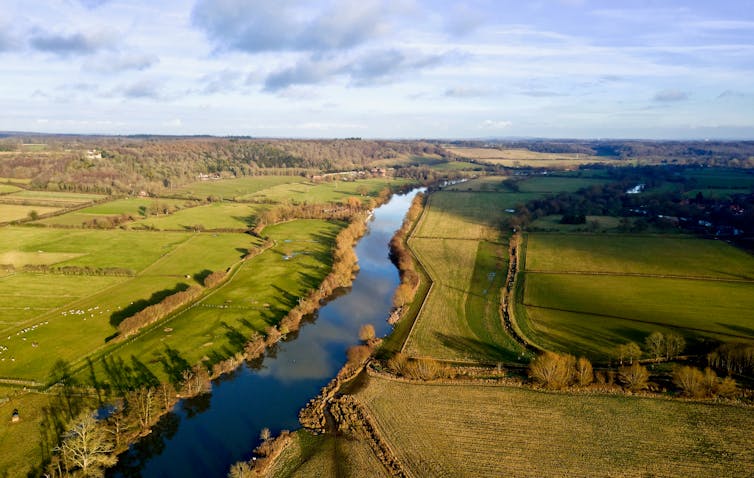
In Britain, for instance, 1,000 years of change has meant 97% of rivers are fragmented by barriers like weirs. Things accelerated after World War I, with 36% of the river network of England and Wales, some 35,500km, subject to major modifications. And these are only the documented changes – much more was routinely maintained, such as the annual removal of silt or vegetation.
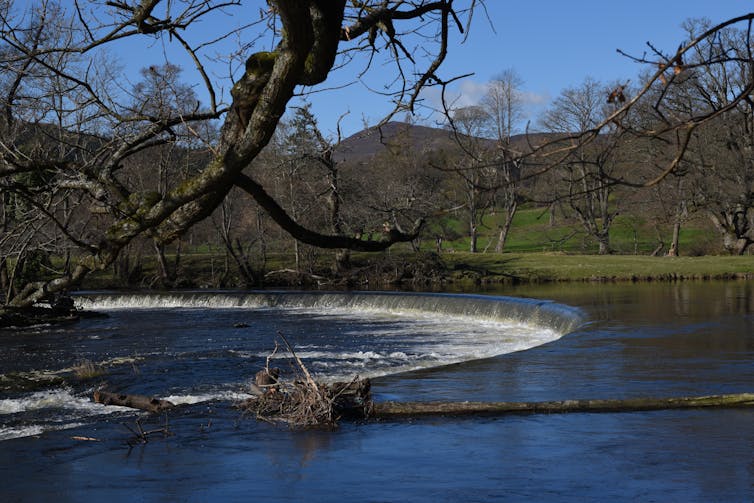

In the early 1990s, I visited every flood defense office in England and Wales as part of a study asking how much sediment is removed from rivers, how expensive it was, and why we were doing it. It became clear that it was costly, and in many cases, it was done simply because “that is what happens on October 15” – and woe betide you if you were late because the locals expected it. This expectation of river cleansing is still apparent today in calls to dredge rivers after a major flood or sometimes to push gravel back into them.
There has been some increase in river restoration (or “re-wiggling”), with more than 2,500km restored in the UK since the early 1990s. However, this represents less than 3% of the highly damaged river network, and much more needs to be done. Though the sewage crisis dominates headlines in the UK, rivers’ physical modification also matters.
The physical form of a river
The “look” of a river isn’t just aesthetics – things like the number and shape of channels, gravel shoals, and sandbanks, or the presence of vegetation or an eroding riverbank all affect how it acts as an ecosystem.
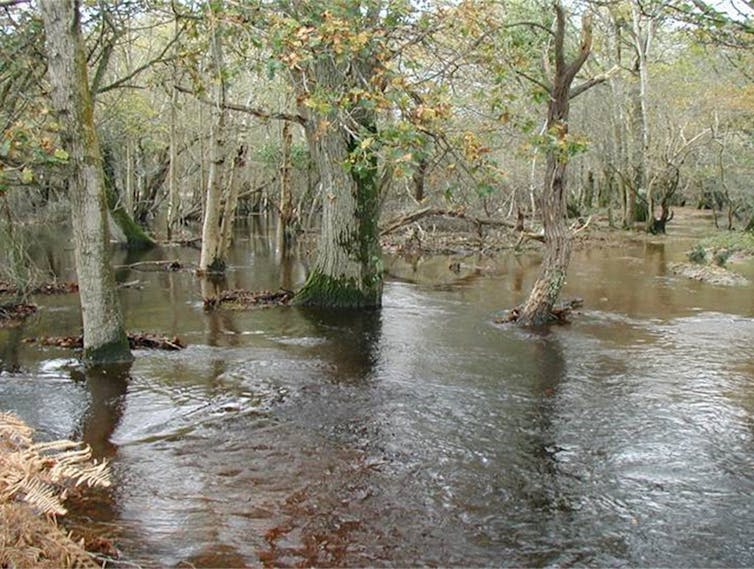

More complex and “messy” rivers tend to store and slow the flow of water, sediments, and nutrients. This creates a better habitat for plants and animals. It also means these rivers don’t strip as many nutrients from the surrounding landscape and are able to store more carbon in the form of living and dead plants (as peat, for example). Messy rivers release water slowly like a sponge, protecting against floods and droughts.
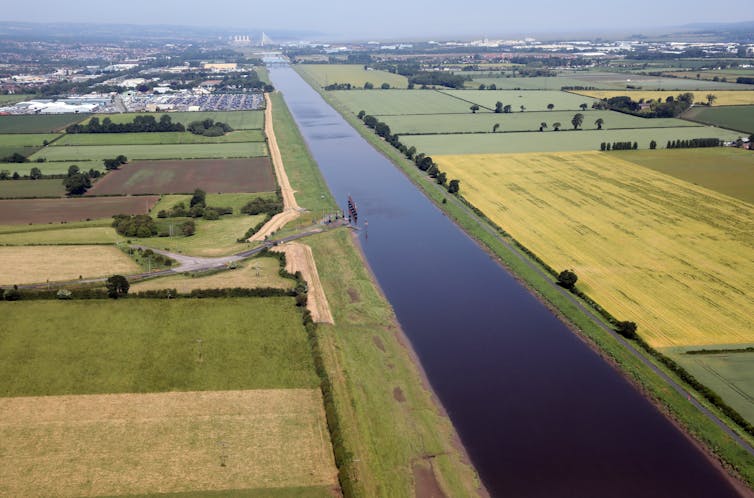
That said, modified rivers can provide efficient transport of bulk goods via shipping; in some cases, they can protect from floods and provide hydroelectricity and food security for millions of people. The restoration of more natural rivers, therefore, involves trade-offs. As far back as 2004, a government report concluded that the UK needed to do something other than build higher and more expensive flood defenses in the face of a future of more extreme and frequent floods. But too often, the multiple benefits provided by more natural rivers are ignored in these discussions.

Neil Mitchell / shutterstock
One option is to work more with nature to deliver benefits from our rivers and floodplains that are not simply based on food security, home building, or flood protection. People want to engage with nature, and recent studies show it is good for us. But first, we must learn to tell the story of how our rivers came to look the way they do and why natural rivers can benefit us all. At the very least, a better understanding of what we have lost and what the alternatives could be will offer a more balanced argument for or against more natural rivers.
Britain’s “riverscape” is the product of centuries of modification. Some of this is here to stay – no one is suggesting turning London back into a floodplain, for instance, and we still need food to protect properties. But we also need a more sophisticated understanding of why allowing some rivers to return to their natural form and processes is vital to our future and to the future of our ecosystems.
David Sear, Professor in Physical Geography, University of Southampton
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.




Comments are closed.