400 Years – Estimated decomposition time for Plastic Beverage Holder
Malcolm David Hudson, University of Southampton
In early December 2017 , he United Nations Environment Programme in Nairobi announced a resolution on marine litter and microplastics. The move was widely welcomed as the emerging “plastic oceans” crisis has become starkly clear.
It is estimated that 8m tonnes of plastic waste finds its way in to the ocean each year, and it is notoriously difficult to remove. The impacts are increasingly apparent: great rafts of plastic are congregating in ocean gyres, blame games have broken out between neighbouring countries, and marine species face poisoning from the associated toxins.
Microplastics kill the plankton that underpin the marine food chain. This 6mm long arrow worm has eaten a microfibre that has blocked its gut. #BluePlanet2 @BBCEarth pic.twitter.com/QnPklpovsM
— Dr Richard Kirby (@PlanktonPundit) December 10, 2017
There may even be direct risks for humans, especially the 400m or so poor people who depend critically on fish for their food. As yet fisheries are more threatened by over-exploitation and climate change, but we are now finding plastics in our marine ecosystems and even in food like mussles and oysters.
Timely – but not binding
Given the urgency of the problem, a more decisive global leadership is needed and so the UN’s announcement is certainly timely. Its resolution on marine litter and microplastics is the first genuine global attempt to tackle the problem. It aims to eliminate marine litter in the long term, urging counties to take action by 2025, to “prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds” and “encourages” them to “prioritise policies” that “avoid marine litter and micro plastics entering the marine environment”. Among other promising points, an international working group will be set up to seek legally binding options to tackle marine litter, and it is encouraging to see that almost 40 countries have signed up to the voluntary #CleanSeas campaign since its launch in February 2017.
In some parts of the ocean it’s estimated that there are over half a million pieces of plastic for every square kilometre#BluePlanet2 pic.twitter.com/RoWEFGXt3w
— BBC Earth (@BBCEarth) December 10, 2017
The elephant in the room here is the lack of any binding targets. Under pressure from key players like the US, China and India, UNEP has backed off putting in targets or binding commitments, although it was reported that the US was at least engaged in the discussions. It is worth noting that China is the biggest emitter of plastic marine litter and along with the US and India has a very large plastic manufacturing sector.
Alarming parallels
There are alarming parallels with the past two decades of attempts to tackle climate change. Evidence that greenhouse gases emitted by human activities were causing more energy to be trapped in our atmosphere has been increasingly clear since the mid 1990s, but vested interests combined with the need for equitable treatment of developing countries means that progress has been painfully slow – so slow that it will now be much harder to stay within the 2°C limit that scientists view as potentially manageable for future generations. Even now, while the evidence is clear and the impacts are painfully apparent round the world, the US has backed out of the 2015 Paris agreement.
But we are are capable of better. In the 1970s and 80s we faced another major environmental threat. Pollutants used in refrigerants (chlorofluorocarbons, or CFCs for short) were damaging the ozone layer, which acts as a protective screen from the worst of the sun’s ultraviolet rays. Alarm bells were ringing as skin cancers increased, and scientists predicted a catastrophe within decades.
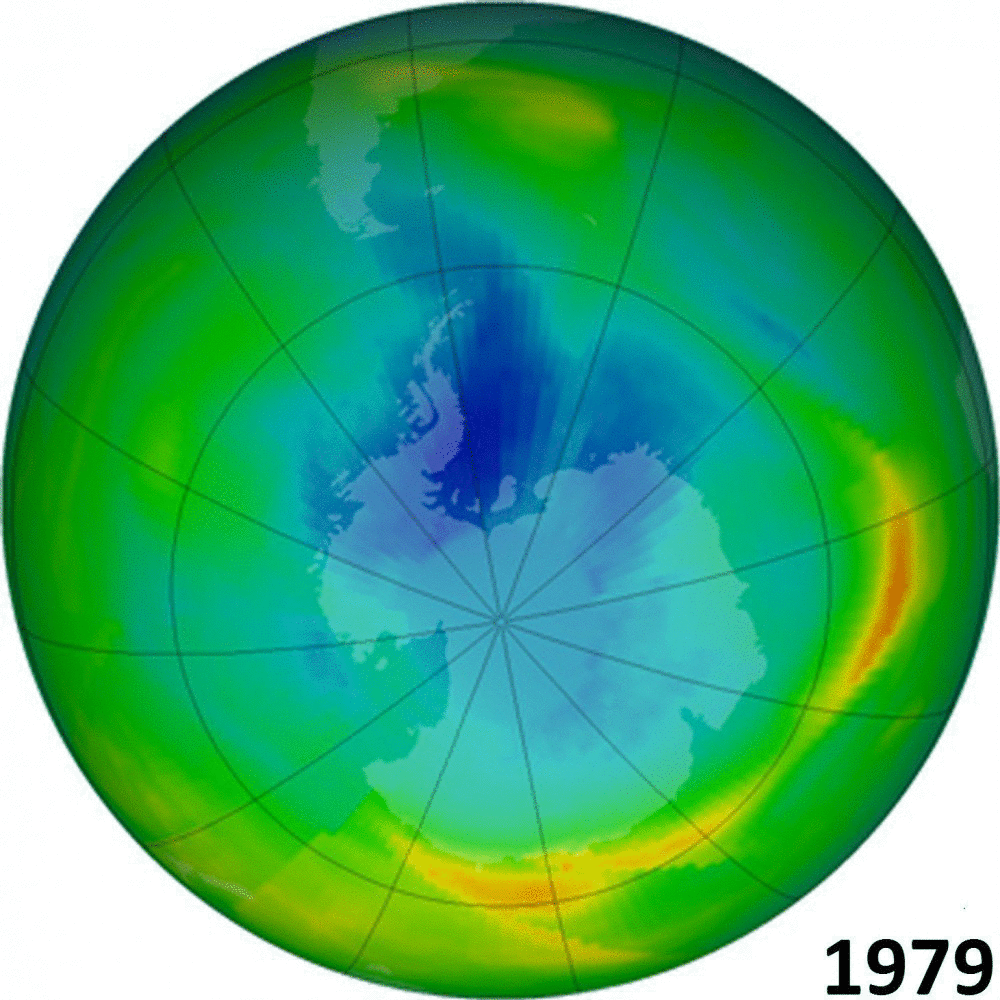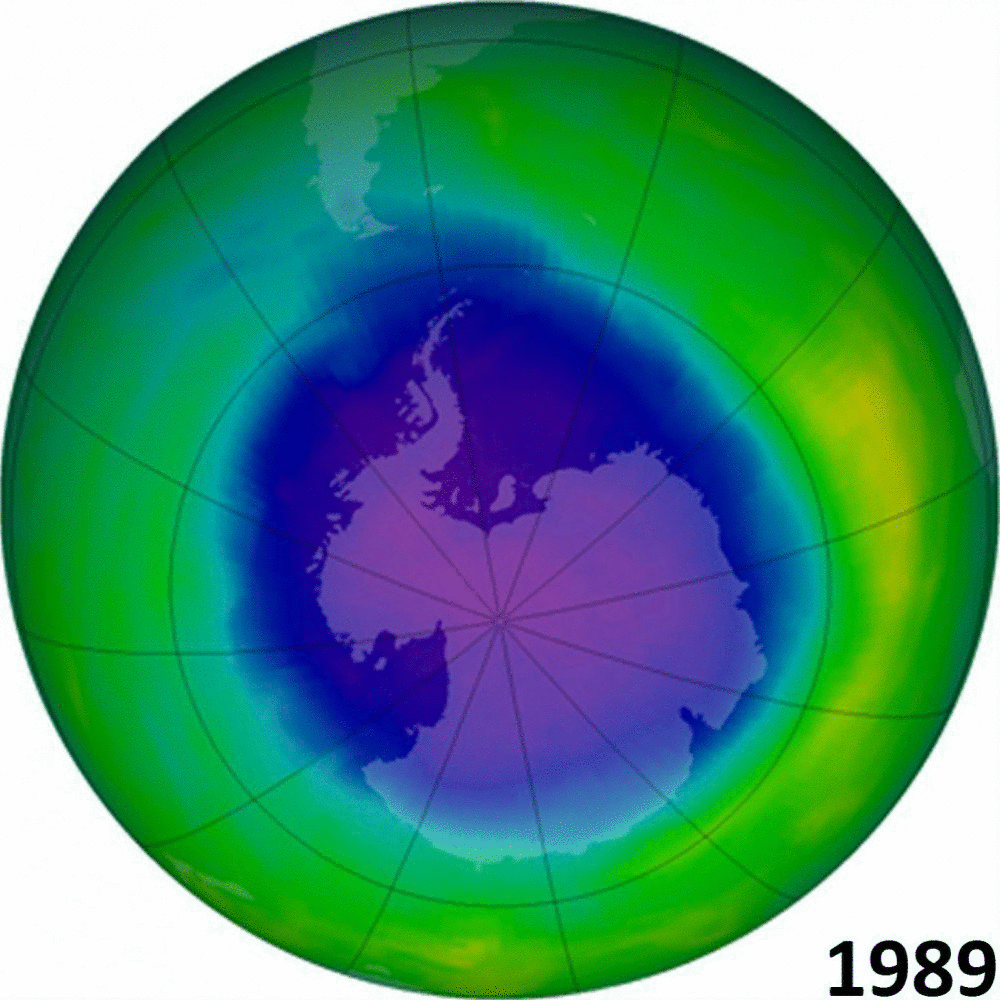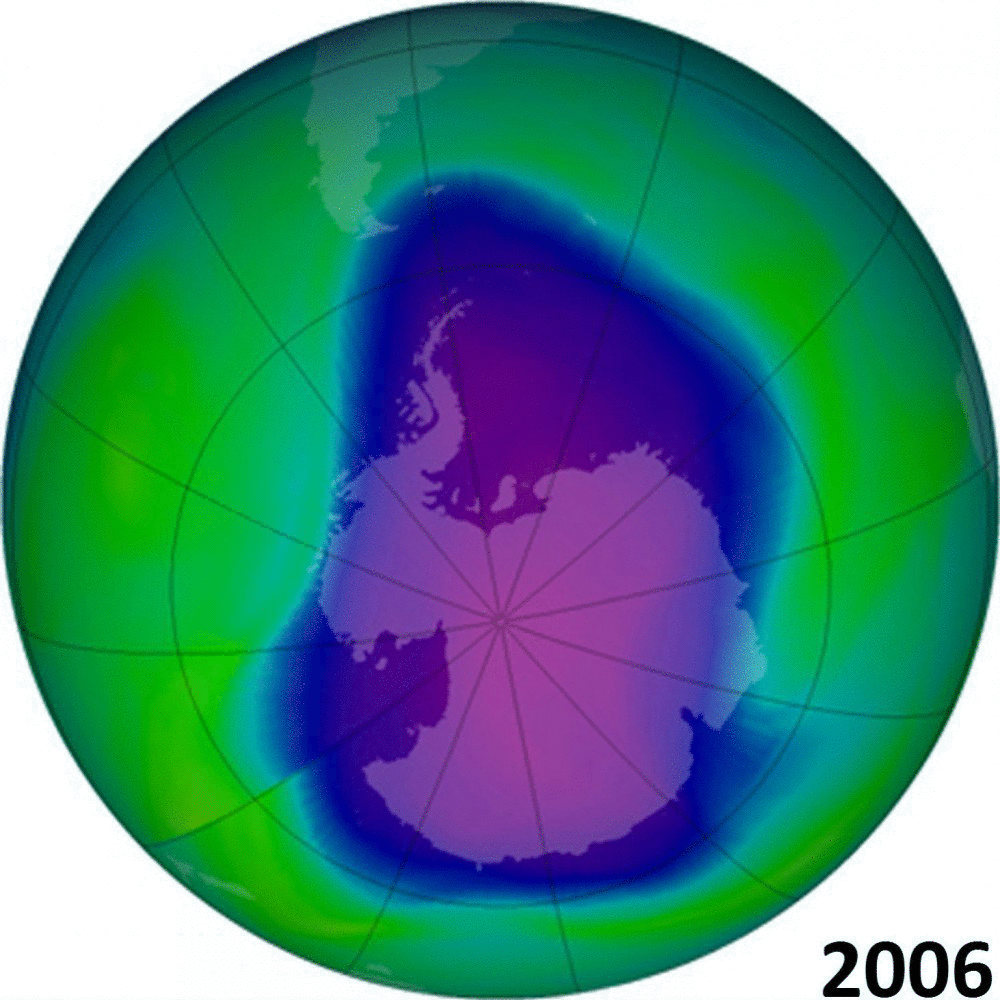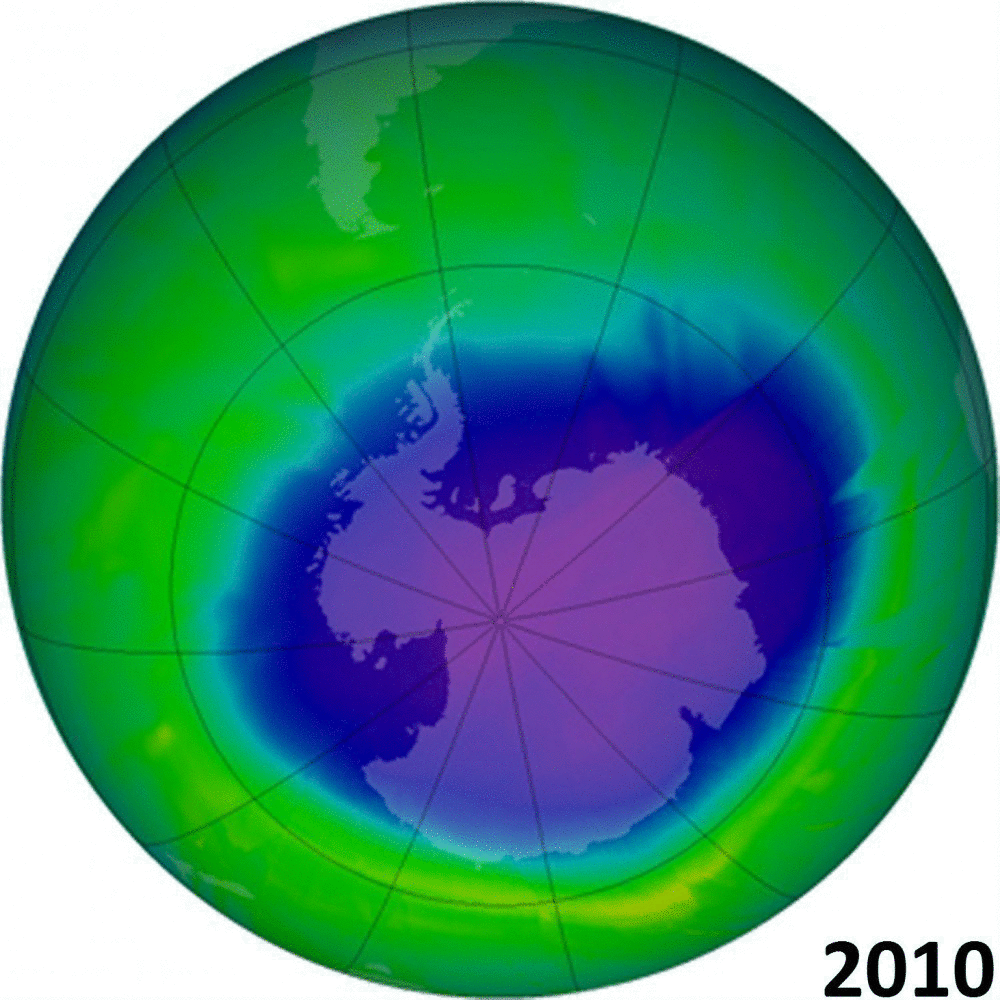
That time, despite the now-familiar lobbying and stalling by industry, who argued that the science was uncertain and that more evidence was needed, the world got together. The Montreal Protocol was agreed in 1987 and since then the harmful chemicals have been phased out or managed more effectively. We have seen the ozone layer recovering towards pre-1980s levels and, in a positive unintended consequence, the phasing out of chemicals that are also potent greenhouse gases.
We humans have a mixed track record. The recovering ozone layer shows that we can, if we have the will and the leadership, get to grips with even the most wicked of environmental problems and turn things round. But, as our attempts to deal with climate change have shown, progress can be slow and getting everyone working together remains fraught with difficulty.
We should not forget that plastics have revolutionised our lives – I am typing this on a plastic keyboard, for instance, while wearing a plastic fibre fleece, and looking through plastic lenses in my glasses. Any change will be tough and could have economic consequences.
![]() But however important plastic seems to our lives, we depend even more on the health of the oceans for our well-being and for that of the planet. Right now attempts to get the world together to deal with plastic waste and ocean pollution are at a crossroads; at least it’s good news we have made it this far.
But however important plastic seems to our lives, we depend even more on the health of the oceans for our well-being and for that of the planet. Right now attempts to get the world together to deal with plastic waste and ocean pollution are at a crossroads; at least it’s good news we have made it this far.
Malcolm David Hudson, Associate Professor in Environmental Sciences, University of Southampton
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.
Blue Planet academic consultants: the message humanity cannot afford to ignore
Blue Planet academic consultants: the message humanity cannot afford to ignore




17 Comments
Pingback: relaxing sleep
Pingback: musica para malhar
Pingback: https://9966003.xyz/2024/02/03/219/
Pingback: pilates woodland hills
Pingback: สมัครบาคาร่า lsm99
Pingback: อุปกรณ์ไอที
Pingback: fiwfans
Pingback: steenslagfolie
Pingback: มรกตโคลัมเบีย
Pingback: dultogel 4d login
Pingback: thai massage in Hamburg
Pingback: ข้อดี – ข้อเสีย Lotto World
Pingback: chat rooms
Pingback: Sbo
Pingback: link
Pingback: no789fun
Pingback: ซื้อหวยกองสลากพลัส