WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange in a police van, after his arrest by British police, in London, April 11, 2019. Photo: REUTERS/Henry Nicholls
“Assange has been a difficult guest for seven years. His continuous communication with the outside world and the way he wrote himself into the legend of the last US presidential elections would certainly have been against the intentions of Ecuador in granting him extraterritorial asylum.
Six weeks before the anti-secrecy organization WikiLeaks published an archive of hacked Democratic National Committee emails ahead of the Democratic convention, the organization’s founder, Julian Assange, foreshadowed the release — and made it clear that he hoped to harm Hillary Clinton’s chances of winning the presidency.
In an interview June 12, 2016, Mr. Assange told a British television host, Robert Peston of the ITV network, that his organization had obtained “emails related to Hillary Clinton which are pending publication,” which he pronounced “great.” He also suggested that he not only opposed her candidacy on policy grounds but also saw her as a personal foe.”

WikiLeaks and Assange are central in Robert Mueller’s Report On The Investigation Into Russian Interference In The 2016 Presidential Election. The first redactions due to “Harm to Ongoing Matter”, in the Report appears already in its list of content.
Quote from article by https://theconversation.com/julian-assange-q-a-wikileaks-founder-arrested-in-london-115325
Kathy Kiely, University of Missouri-Columbia and Laurel Leff, Northeastern University
These days, anybody with an internet connection can be a publisher.
That doesn’t make everybody a journalist.
This distinction has become more important than ever in light of two recent events.
One was the arrest of WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange. The other was a proposal by lawmakers from Georgia, the Peach State, that looked more like an export from the Georgia that was part of the Soviet Union: a so-called “ethics in journalism” act that would have imposed onerous new requirements and potential civil penalties on reporters.
As soon as news broke of Assange’s potential extradition to the United States for trial on charges of conspiracy, his allies began campaigning to make him a Fourth Estate martyr.
“Every journalist in the world” should be speaking out on Assange’s behalf, said Intercept editor Glenn Greenwald. Another fugitive leaker of U.S. government secrets, Edward Snowden, tweeted that Assange’s arrest represents “a dark day for press freedom.”
As two journalism professors who practiced the craft for many years before becoming teachers of it, we know firsthand how powerfully reporters are drawn to unpopular causes. It’s an admirable reflex that often makes for great journalism and a better society.
But granting Assange journalist status is beyond problematic: It’s likely to draw more attacks on press freedom such as the Georgia lawmakers’ thinly disguised attempt to sanction and ostracize journalists whose work they don’t like.
Standards differentiate journalism
As the Pew Research Center has shown, journalists already are an endangered species. In part that’s because the digital revolution eliminated the advertising that subsidized newsrooms.
But as the Knight Foundation has documented, those financial problems are compounded by a credibility crisis.
“Most U.S. adults, including more than nine in 10 Republicans, say they personally have lost trust in the news media in recent years,” the foundation reported in September 2018.
There may be lots of reasons for this but it certainly doesn’t help that more Americans are getting their news from social media feeds that intermingle journalism with the kind of propaganda that is keeping Facebook busy playing whack-a-mole with trolls, sent a deluded man with a gun to a neighborhood pizza restaurant in Washington, D.C. and stoked protests on a college campus with incendiary fake tweets.
As a profession, journalists are becoming increasingly aware of the need to advocate for, and try to uphold, standards that differentiate them from those who merely make information available.
The New York Times did exactly that in 2010, when it ran stories based on documents obtained from WikiLeaks. An editor’s note explained why the Times believed publication to be in the public interest, how the paper gave government officials a chance to respond before publication, and how it redacted “information that would endanger confidential informants or compromise national security.”
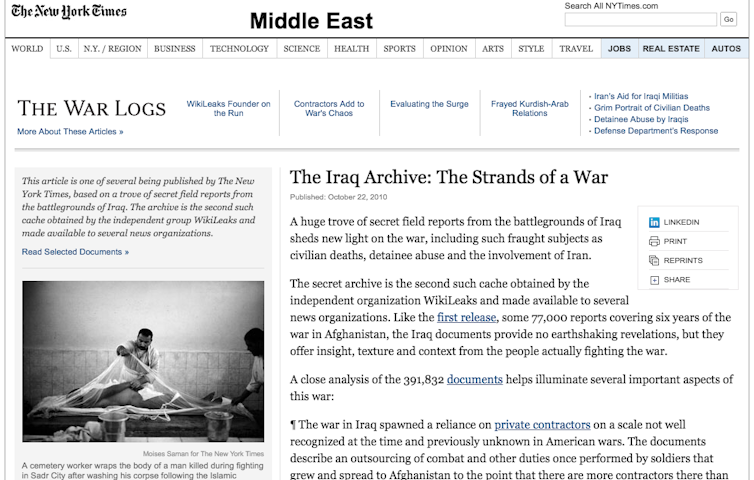
New York Times screenshot
The Times wrote that it shared its rationale for making the redactions with WikiLeaks “in the hope that they would similarly edit the documents,” but Assange does not appear to have been impressed. He followed no journalistic practices or journalism ethics in subsequent data dumps.
When WikiLeaks posted the emails of Democratic National Committee and Clinton campaign staffers in 2016, it included home and email addresses, and credit card, Social Security and passport numbers, as well as the details of a staffer’s suicide attempt.
Deserving a privilege
In insisting that journalists should not be prosecuted for disclosing classified information or for refusing to reveal confidential sources to grand juries, the press is seeking a privilege in both the legal and literal meaning of the term.
It’s not a privilege if everyone gets it. There has to be something special about what journalists do, and how and why they do it, that makes them worthy of a privilege that others don’t receive.
So far, the charges against Assange are for conspiring to hack into a Pentagon computer network. As Gabe Rottman of the Reporters Committee for Freedom of the Press writes, that “isn’t something that a newsroom lawyer would counsel a reporter to do.”
Rottman’s measured analysis also notes another concern for data reporters: The 1984 law at the heart of the Assange indictment, the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act could, if interpreted in an overbroad fashion, endanger journalists (or other members of the public, such as academics) who use computer programming to “scrape” otherwise hard-to-analyze information from public government websites. But that’s not the issue here.
Nor, significantly, is Assange charged with publishing on the WikiLeaks website documents obtained through that hack. Legal decisions have long offered a great deal of protection to those who publish information, nowhere near as much to those who seek access to government information or facilities, and virtually none to those who steal information.
The best way for press and press freedom organizations to ensure the Assange case doesn’t set precedent that interferes with the public’s right to access important information – even information the government doesn’t want to reveal – is through friend of the court briefs.
Editorial boards rushing to make Assange a poster boy for press freedom, as former New York Times lawyer and First Amendment icon James Goodale recently suggested they should, will only provoke lawmakers into pushing more proposals like the journalism review board. Thankfully, that died earlier this month when the Georgia legislature adjourned without acting on it.
Journalists are justifiably concerned that more such attacks are likely. Heading them off will require journalists to help their audience understand and appreciate the professional and ethical standards that distinguish real reporters from mere disseminators.
In a digital age, the latter are a dime a dozen. It’s the reporters who need to be protected and defended.![]()
Kathy Kiely, Professor and Lee Hills Chair of Free Press Studies, University of Missouri-Columbia and Laurel Leff, Associate Professor of Journalism, Northeastern University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.



5 Comments
Pingback: sleep music
Pingback: deep sleep
Pingback: piano music
Pingback: jazz cafe
Pingback: fairfax psychiatry