
Simon Kingham, University of Canterbury
The Dutch have long been recognized as leaders in cycling. Denmark is not far behind, with more bikes than cars in its capital Copenhagen. This is the result of many years of investment. Even the UK, with less of a cycling tradition, is investing and showing growth in cycling.
New Zealand is starting to follow suit. The Emissions Reduction Plan, released last week, includes NZ$350 million to encourage walking, cycling, and public transport.
Investment in cycling is often motivated by the need to curb emissions and increase rates of active transport. But the backlash can sometimes seem as large as the level of spending.
New Zealand spends around $5 billion per year on transport. On average, over the past decade, 41% was spent on maintaining existing roads, 38% on building new roads, 17% on public transport, and 1.7% on walking and cycling.
Some critics argue cyclists do not pay for cycle infrastructure.
But transport funding comes from several sources, including central government funds such as fuel excise duty (paid on petrol purchased), road user charges (paid by diesel vehicle owners), vehicle registration and licensing, and local government funds from rates. One-off investments have come from the NZ Upgrade Programme and the Provincial Growth Fund.
Many of these sources come from general taxation, which cyclists pay. Most people who commute by bike usually also own a car and therefore pay for registration and licensing.
Increasing the number of cyclists will benefit the economy since research shows cities with more physically active people are more productive. The evidence for investing in cycle infrastructure is compelling.
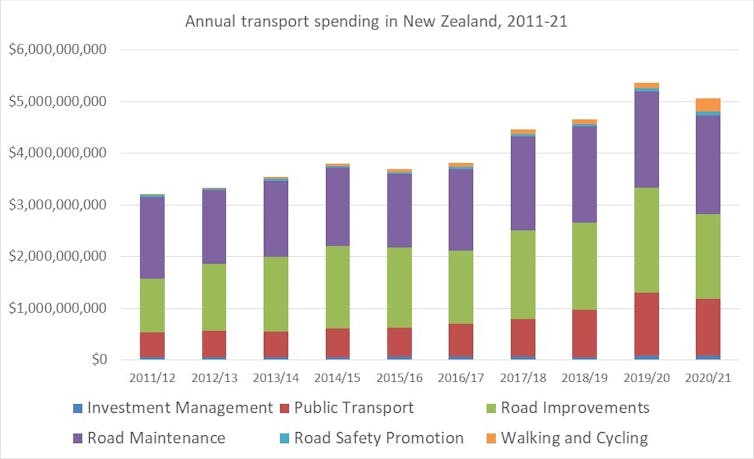
Road building and maintenance take up most of the transport funding, with less than 2% spent on cycling and walking infrastructure. Author provided
Health benefits from cycling
Active commuting has been shown to reduce the risk of disease and enhance mental health. Research has even found that cycling is the happiest way to travel.

Shutterstock
A recent review of over 170 studies found places designed to encourage walking and cycling have lower rates of obesity and diabetes.
New Zealand research confirms overseas findings that cyclists are exposed to healthier air than car drivers. Segregated cycle lanes, even a small distance from traffic, improve air quality.
Some people raise concerns about the safety of cycling, with data showing injury and fatality rates are higher for cyclists for each kilometer traveled. However, the more people cycle, the safer it becomes for all road users.
Build it and they will come
The standard tool to inform transport decisions is the benefit-cost ratio. A UK government report found the average benefit-cost ratio for walking and cycling projects delivers benefits 13 to 35 times the cost.
In New Zealand, transport planners estimate money spent on high-quality cycling infrastructure yields benefits between ten and 25 times the costs.
bbbb
“A new cost-benefit study in New Zealand finds that investments in cycling & walking facilities outweigh the costs of building them by 10 to 1. The research found that the most important economic benefits were health gains from use of active transport.” https://t.co/JEGofP4vAj pic.twitter.com/WQ4vI3zx1N
— Brent Toderian (@BrentToderian) January 10, 2022
Research clearly shows the biggest barrier to cycling is perceived safety. Segregated cycleways are key to feeling safe, and infrastructure should be a mix of separate cycling facilities along roads with heavy traffic and at intersections, combined with extensive traffic calming of residential neighborhoods, coupled with lower speed limits.
The physical separation from traffic comes at a higher cost and these expensive projects tend to attract the headlines, such as the proposed Auckland Harbour crossing.
But many cycle routes use lower speeds and simple traffic management to create a cycle-friendly environment. Overall, cycleways are cheap compared with other transport infrastructure.
Evidence shows the number of people cycling is related to the quality and quantity of infrastructure provided. This has been demonstrated in the US, UK, Denmark, and most recently in a European study that examined the impact of temporary cycle infrastructure “popping up” as a COVID transport solution.
Registration for cyclists
The issue of whether cyclists should be registered or licensed has generated debate. The arguments for registration include:
- some form of registration would provide legal accountability
- registration could raise funds to pay for cycle infrastructure
- the process would include a cycling test to improve cyclists’ safety.
The arguments against include:
- complication and confusion deciding who and what to include (children, tricycles, people who never ride on the road, etc)
- creating a barrier to people on low incomes who use a bike because they cannot afford a car
- cyclists already paying for cycle infrastructure through their taxes.
Ultimately, the main reasons against registration are bureaucracy and cost. The UK government concluded the cost and complexity of introducing such a system would significantly outweigh the benefits.
Cycleways and business
One frequent complaint is that when cycleways replace on-street parking, businesses suffer. But research does not support this.
According to Bloomberg CityLab, multiple studies have reached a similar conclusion: replacing on-street parking with a bike lane has little to no impact on local business, and in some cases might even increase business.
Evidence from the US suggests people who travel by bike spend more. A small New Zealand study supports this.
A study in London found that “an increase in cycling trips significantly contributes to the emergence of new local shops and businesses”. In New Zealand, there is some evidence a growing number of businesses appreciate the benefits of cycleways.
Safety is the main barrier
Poor weather is a barrier for some people, but not one of the most significant ones. Rates of commuter cycling do not vary dramatically by season. Cycling rates in Christchurch in winter are only 10% lower than during other times of the year.
While US research has shown cycling declines in bad weather, a New Zealand study calculated that someone cycling to work every day in the main cities would only get wet six times a year.
What really stops some people from hopping on a bike is that they don’t feel safe cycling in traffic. As Chris Boardman, an Olympic gold medallist cyclist and now commissioner for Active Travel England said, we can tackle our biggest crisis, and “all we have to do is make nicer places to live”.![]()
Simon Kingham, Professor, University of Canterbury
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.




6 Comments
Pingback: musica eletronica 2023
Pingback: คลินิกสมุทรสาคร
Pingback: ฟอกไตสมุทรสาคร
Pingback: ปรึกษาคดี
Pingback: แผ่นติดหลังคา HPMC
Pingback: รับสร้างบ้านหาดใหญ่