Ariboen / shutterstock
The city of Cali, in Colombia, is hosting the UN’s 16th biodiversity summit, known as Cop16. The summit, which runs until Friday, November 1, is focused on how countries will fulfill previous pledges to protect at least 30% of the world’s land and water and restore 30% of degraded ecosystems by 2030.
It’s a noble aim, yet Colombia shows just how far we must go.
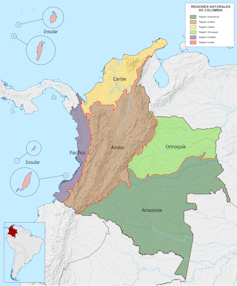
If you travel southeast from Cali, over the Andes mountains, you drop into the Amazon basin. From there, rainforest stretches hundreds of kilometers to the border with Brazil – and far beyond. This rainforest is the main reason Colombia ranks as the fourth most biodiverse country in the world. Nowhere else has as many species of birds. Only Brazil and China have more trees.
However, the region is experiencing an environmental crisis. I recently completed a PhD on the northern Colombian Amazon, in which I tracked how the rainforest is fast being deforested and turned into pastures for cattle ranches. I particularly examined how this affects hotspots of plant and animal life in rugged valleys on the Amazonian side of the Andes—spectacularly biodiverse places even by Colombian standards—and what can be done to protect them.
It is not easy to do such work in this part of the world—the NGO Global Witness ranks Colombia as the most dangerous country for environmental defenders. While documenting legal and illegal cattle ranching, I was often reminded to be aware of precisely who I was contacting and to be wary of which questions I was asking.
Activists and researchers often face violence from those who profit from deforestation, and I had to work closely with organizations and authorities that secure their safety. Very harrowing experiences are not uncommon.
Despite these risks, many continue their efforts, driven by a deep commitment to protecting the Amazon and its biodiversity. Their bravery only underscores the urgent need for stronger protections and enforcement.
Peace led to more deforestation
For decades, the region was controlled mainly by the FARC guerrilla army. The Farc was largely funded by kidnappings and the drug trade and wasn’t interested in large-scale farming.
All this changed after the Colombian government signed a peace agreement with the FARC in 2016. Since then, deforestation has increased, as legal and illegal land tenants have acquired land for farming through “sustainable development” practices. This mainly involves turning forests into pasture for cattle, the main driver of deforestation across Latin America.
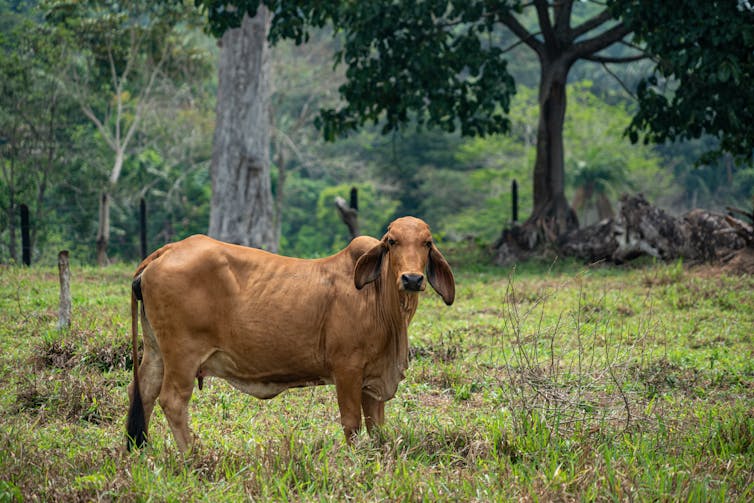

Things peaked in 2018 when 2,470 square kilometers of forest were lost in Colombia—equivalent to a circular area more than 50 kilometers across. Rates of deforestation have reduced slightly since then (though the data isn’t very reliable) but appear to be increasing once again in 2024.
The recent increase might be attributed to the demand to produce more coca or rear more cattle and pressure from extractive industries like mining. The spread of roads and other infrastructure into the rainforest has also opened up new opportunities.
Billions more are needed to stop deforestation
In its 2018 Living Forest Report, the WWF included Colombia’s Chocó-Darién and Amazon forests in its list of 11 “deforestation fronts” across the planet. These fronts are projected to be where the largest concentrations of forest loss or severe degradation will occur until 2030.
It’s no wonder Colombia’s environmental crisis has drawn international attention. Countries like Germany, Norway, and the UK have supported their efforts to reduce deforestation, pledging about €22 million under the UN’s reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation scheme (known as REDD+). This is a good start, but much more is needed.

Indeed, the Global Biodiversity Framework, the international treaty that underlies the Cop16 negotiations in Cali, estimates that protecting biodiversity will require an extra US$700 billion each year.
Therefore, an important issue at the summit is how to mobilize sufficient financial resources, particularly for developing countries. The previous global biodiversity summit in Canada in 2022 established that wealthy countries should provide US$30 billion annually to low-income countries by 2030.
Before this year’s summit, countries were expected to submit new national biodiversity plans detailing how to meet the 30% protection goals. Most, including Colombia, failed to do so. Despite this setback, delegates in Cali will hopefully develop robust mechanisms to monitor progress and ensure countries are held accountable for meeting their targets.
About 80% of countries fail to submit plans to preserve nature ahead of global summit
Other critical issues include reforms to benefit small-scale farmers in the Amazon. The region’s current economic model is centered on reshaping the land and extracting resources, but it has not generated prosperity for these more sustainable farmers. That same economic model has also failed to protect the forest itself.
The summit should also work towards recognizing Indigenous peoples’ rights and traditional knowledge, including their voices in policy decisions, and must address violence against environmental defenders.
These are all huge issues in Colombia and any country where cattle farmers are eyeing pristine rainforests. The summit in Cali represents a great opportunity for the world to tackle the dual biodiversity and climate crisis seriously.
Jesica Lopez, PhD Candidate, Centre for Environmental and Climate Research, Lund University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.




Comments are closed.